Bitumen vs Asphalt: Full Comparison, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages
When it comes to road construction, roofing, waterproofing, and paving projects, two terms are frequently mentioned—bitumen and asphalt. While often used interchangeably, these materials have distinct properties, uses, and performance characteristics. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore bitumen vs asphalt, their applications, advantages and disadvantages, and provide a detailed comparison to help buyers, engineers, and contractors make informed decisions.
Whether you’re a bitumen supplier, bitumen trader, bitumen seller, or contractor, understanding the differences is key to selecting the right material. Let’s dive into it.
What is Bitumen?
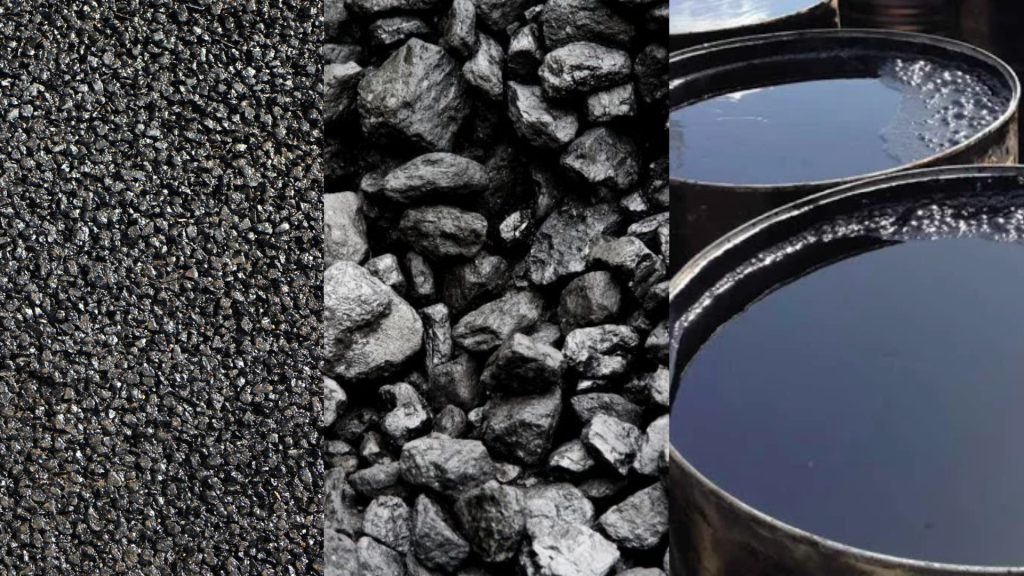
Bitumen is a black, sticky, viscous material derived from crude oil distillation. It is a hydrocarbon substance and plays a vital role in waterproofing and binding aggregates in road construction. The bitumen formula is complex, consisting of various hydrocarbons with high molecular weights.
Types of Bitumen:
-
Penetration Grade Bitumen (e.g., bitumen 40/50, bitumen 60/70, bitumen 80/100)
-
Viscosity Grade Bitumen (VG30, VG40)
-
Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB)
-
Bitumen Emulsion
-
Bitumen Liquid (Cutback Bitumen)
Bitumen is often supplied in bitumen drums, in bulk, or as a bitumen emulsion for various applications.
What is Asphalt?
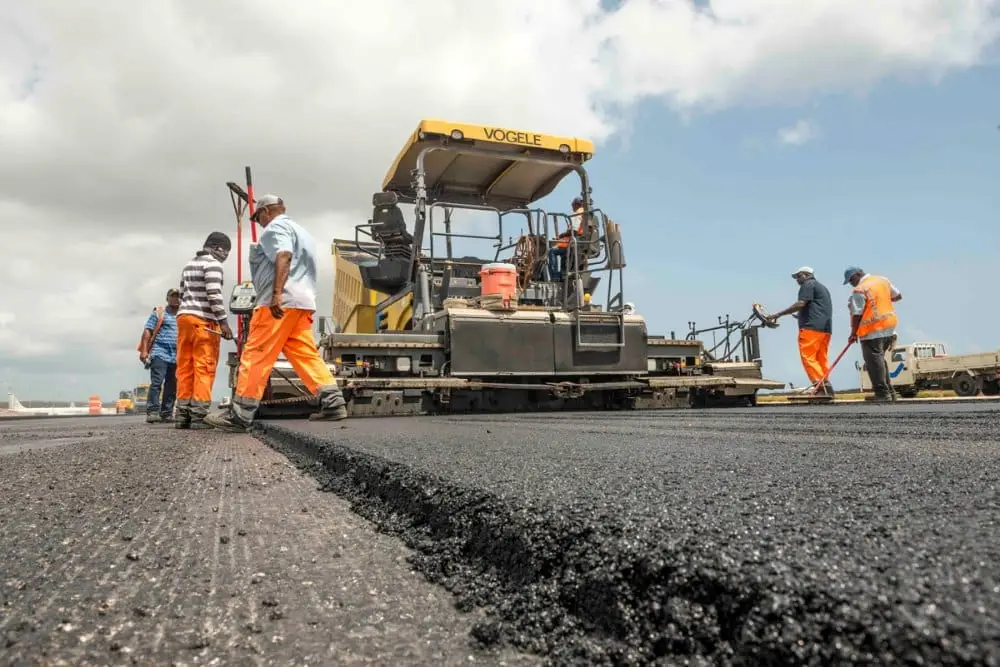
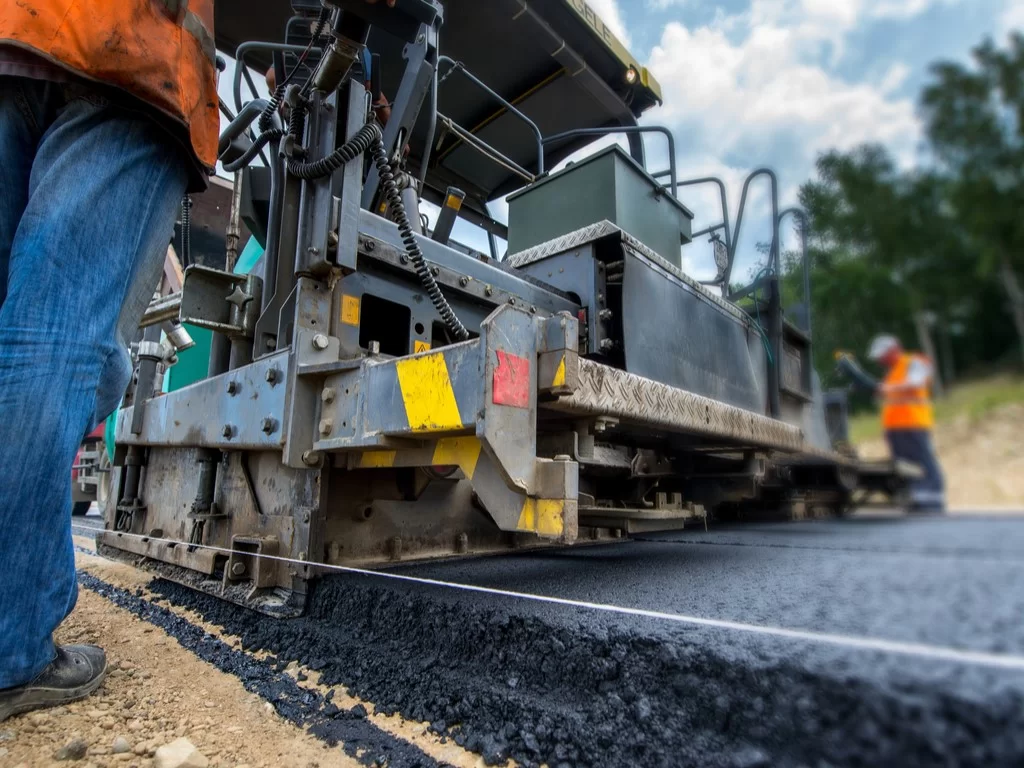
Asphalt, on the other hand, is a composite material composed of bitumen as the binder and a mixture of aggregates like sand, crushed stone, and gravel. Asphalt is essentially the final product used in paving roads, highways, airports, and more.
Asphalt paving is widely recognized for its durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for high-traffic road surfaces.
Bitumen vs Asphalt: Key Differences
| Feature | Bitumen | Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A binding agent derived from crude oil | A mixture of bitumen and aggregates |
| Appearance | Viscous black liquid/semi-solid | Solid mixture (blacktop) |
| Use | Binder in construction, waterproofing, sealing | Used in road surfaces, airport runways |
| Composition | Pure or modified bitumen | Bitumen + aggregates |
| Application | Roofs, waterproofing, bitumen road, sealing joints | Asphalt paving, roads, runways |
| Flexibility | Requires additives for flexibility | Naturally flexible due to aggregate structure |
| Recyclability | Limited | Highly recyclable |
| Installation | Requires heating and mixing | Ready-to-use composite material |
Bitumen Applications
Bitumen application ranges widely across different sectors. Some of the most common uses include:
Road Construction
- Used as a binder in bitumen road layers.
- Penetration grades such as bitumen 60/70 or bitumen 80/100 are most common.
- VG grades such as VG30 / VG40 bitumen are popular in hot climates like Ethiopia and India.
Roofing & Waterproofing
- Bitumen roof sheets and membranes are widely used for waterproofing buildings and flat roofs.
Industrial Applications
- Used in sealing, insulation, and corrosion protection.
- Bitumen liquid or cutback bitumen is often used where heating isn’t practical.
Paving
- Combined with polymers (Polymer modified bitumen) to increase elasticity and performance under extreme temperatures.
Asphalt Applications
Asphalt paving is primarily used for:
-
Highways and city roads
-
Driveways and parking lots
-
Airport runways
-
Racetracks
-
Sports courts
Its composition makes it ideal for load-bearing surfaces due to its strength and ability to withstand high traffic volumes.
Advantages of Bitumen
Versatility – Used in both road and building sectors
Waterproofing – Naturally water-resistant
Cost-effective – Especially in developing countries
Variety of Grades – Including bitumen 40/50, 60/70, 80/100, VG30, and more
Ready Stock Availability – Gulf Petro Vision, a leading bitumen supplier in the Middle East, offer bitumen ready stock in different grades and packaging
Disadvantages of Bitumen
Environmental Concerns – Derived from petroleum
Temperature Sensitivity – Loses elasticity in cold climates
Not Recyclable – Unlike asphalt
Handling Hazards – Requires careful heating and handling
Advantages of Asphalt
Recyclable – Can be milled and reused
Flexible – Withstands temperature and load fluctuations
Fast Installation – Saves time on large projects
Durability – Ideal for highways and runways
Lower Maintenance Cost – Long-term savings
Disadvantages of Asphalt
Higher Initial Cost – Compared to basic bitumen
Surface Cracks – May develop over time if not maintained
Aggregate Shortage – Can increase cost or affect quality
Market Trends and Bitumen Grades
Bitumen demand is rising in African countries like Ethiopia due to rapid urbanization and infrastructure growth. The most in-demand bitumen grades include:
-
Bitumen 60/70 – Ideal for moderate climates
-
Bitumen 80/100 – Used in colder regions
-
Bitumen 40/50 – Suitable for warm climates
-
VG30 / VG40 Bitumen – Common in tropical and monsoon-prone regions
-
Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB) – Growing popularity for performance-based applications
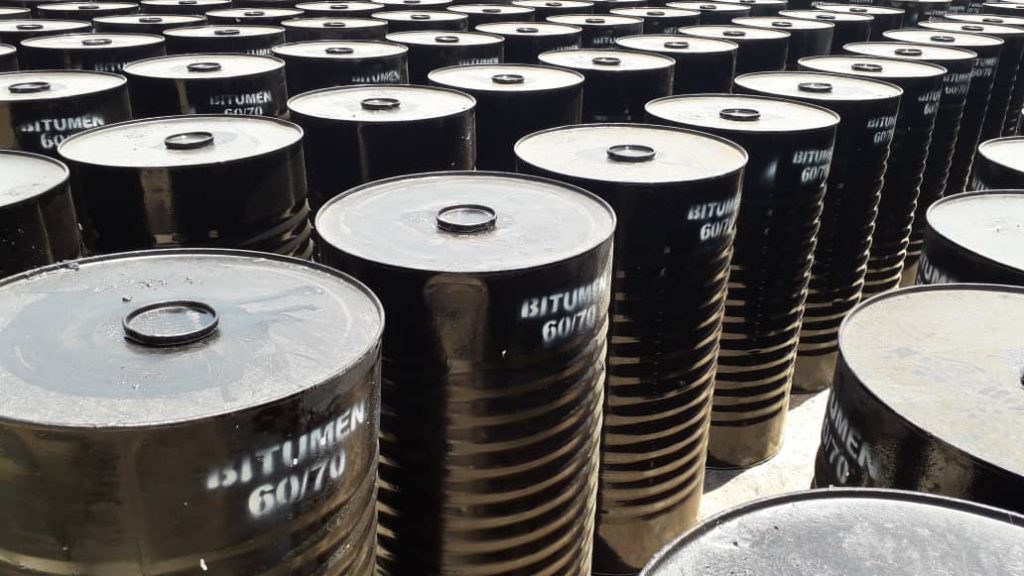
Bitumen Packaging & Supply Chain
The standard supply forms include:
-
Bitumen Drum (180-200 kg)
-
Bulk Bitumen
-
Bitumen Emulsion
-
Cutback Bitumen (Bitumen Liquid)
Global buyers looking to buy bitumen should always consider stock availability, grade specifications, and logistics costs. Checking bitumen online price is now easier than ever, with digital platforms helping streamline sourcing.
Choosing the Right Supplier
Finding a reliable bitumen exporter or bitumen trader is essential to ensuring timely delivery and consistent quality.
Gulf Petro Vision, a reputable bitumen supplier and bitumen seller in the Middle East, is a trusted name in the industry. The company supplies a full range of bitumen grades, including:
-
Bitumen 60/70
-
Bitumen 80/100
-
VG30 / VG40
-
Polymer Modified Bitumen
They maintain bitumen ready stock to cater to urgent orders and offer competitive bitumen price options for buyers in the Middle East, and Asia.
How to Place a Bitumen Inquiry
Before making a purchase, always:
-
Check bitumen application needs
-
Specify the bitumen grade (e.g., bitumen 6070, VG30)
-
Choose the packaging (drum, bulk, jumbo)
-
Compare the bitumen online price
-
Confirm delivery timelines and port handling
To buy bitumen, send your bitumen inquiry to a trusted supplier.
Conclusion: Bitumen vs Asphalt—Which is Right for You?
Understanding the difference between bitumen and asphalt is vital for engineers, contractors, and procurement teams. While bitumen serves as a versatile binding and waterproofing material, asphalt provides the structural strength needed for roads and runways.
Use Bitumen If:
-
You need roofing or waterproofing solutions
-
You’re working in small-scale paving or sealing
-
You’re operating in a region like Ethiopia, where bitumen paving is common
Use Asphalt If:
-
You need a long-lasting road solution
-
You’re constructing high-traffic or load-bearing surfaces
-
You want a recyclable material
Final Thoughts
The bitumen vs asphalt debate depends on your project needs, climate, budget, and logistics. Make sure to source material from a reputable bitumen supplier like Gulf Petro Vision, who not only provides a full range of bitumen grades, but also ensures quality, affordability, and on-time delivery across the Middle East, Africa, and Asia.
For updated bitumen price, stock status, and technical specifications, feel free to contact Gulf Petro Vision or place your bitumen inquiry today.